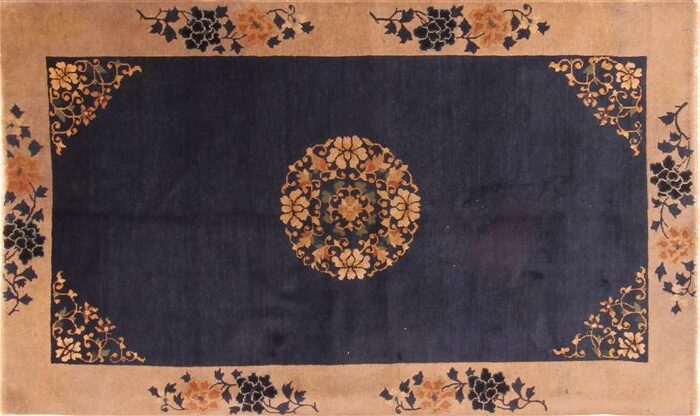
Rugs of China are considered to include those of Manchuria, Mongolia, and Xinjiang. Rugs were primarily woven in northern China. Contemporary Chinese rugs are woven in cooperative factories. There is consistent quality in these rugs due to the use of steel looms, chrome dyes, and objective production standards.
A Chinese saddle blanket from Lop Sanpra was dated to about 100 b.c.e. A few pile rugs have been dated to the Ming dynasty. Domestic pile rug production in China was quite small until production for export began in about 1890. Rug-weaving centers predating rug production for export include Ningxia, Baotou, Suiyuan, and the towns of Gansu. See entries under these names. Commercial rug production for export began late in the nineteenth century in Beijing and about the turn of the century in Tianjin.
Tianjin became the center of large-scale commercial production from about 1910 to 1930 as foreign firms came to dominate the Chinese rug industry. American firms in China included Karagheusin, A. Beshar & Co., Donchian, Avanosian, Kent-Costikyan, Elbrook Inc., Nichols Super Yarn, and Fette-Li. Throughout the early twentieth century, the United States was the largest importer of Chinese rugs. The peak period of rug production and shipment to the United States was 1925. In the early 1930s, rug production was interrupted by the Japanese invasion. Large-scale commercial production was not resumed until the 1960s.
Characteristics of Chinese Rugs
-
Material and Knots
Chinese rugs use the asymmetric knot with occasional use of the symmetric knot in edges and ends of early examples. Chinese rugs are not finely knotted, varying between 30 and 120 knots per square inch. Some early Chinese rugs have asymmetric knots that are offset on warps or skip warps at curving borders of color changes. Early rugs have no warp offset, while later rugs have offset warps, some with closed backs.
The “line” is the contemporary measure of knot density. Woolen carpets are woven in 70, 80, 90, and 120-line qualities. Silk rugs are woven in 120 to 300 line qualities. Pile heights for wool rugs are ⅜, ½, and ⅝ inch. The pile height for silk rugs is ½ inch. The Chinese rug trade designation “Super” means a 90-line rug with ⅝ inch pile height and a closed back.1
Collections
- Chinese Rugs | © Rugman
- Chinese Rugs | © Rugman
- Chinese Rugs | © Rugman